Wireless charging technology has evolved rapidly, transforming the way we power everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. This article dives deep into the history, technology, applications, and future of wireless charging while exploring its benefits, challenges, and the companies driving innovation.
What is Wireless Charging?
Wireless charging, also known as inductive charging, is a process that allows devices to be charged without the need for physical connections. It transfers power from a charging pad or station to a compatible device using electromagnetic fields. By eliminating cables, it offers a convenient, clutter-free way to keep devices charged.
The History of Wireless Charging
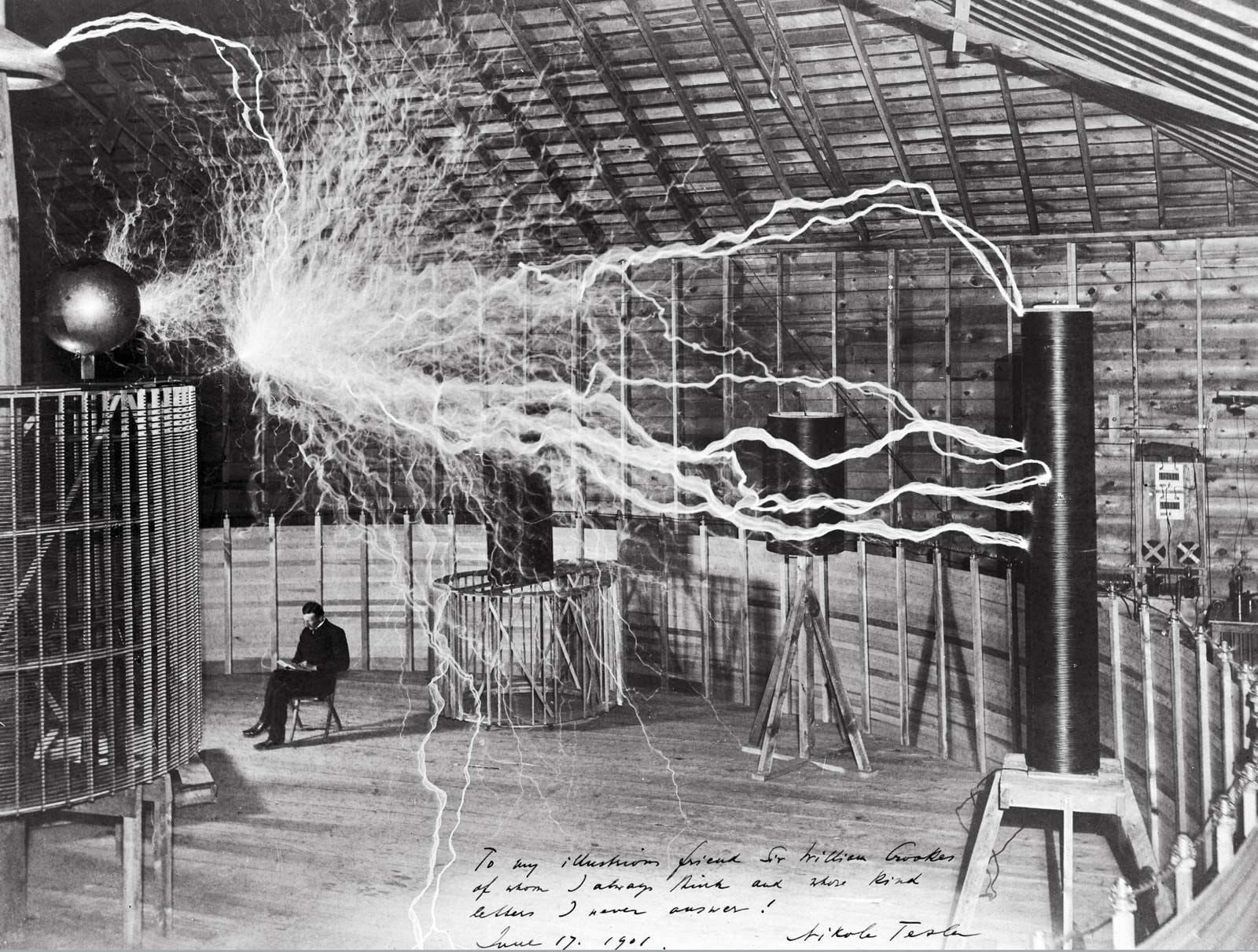

Wireless charging technology dates back to the late 1800s when inventor Nikola Tesla demonstrated wireless energy transfer through magnetic fields. He developed the Tesla Coil, which could wirelessly transmit power over short distances. However, the technology remained impractical until advances in electronics and miniaturization made it feasible for consumer use.


In the early 2000s, wireless charging started making its way into consumer products, initially for small devices like electric toothbrushes. The launch of Qi wireless charging standard in 2008 by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) helped standardize the technology, paving the way for smartphones and other devices to adopt it. By the 2010s, wireless charging became mainstream in consumer electronics, with companies like Apple and Samsung integrating it into their flagship phones.
How Wireless Charging Works?
Wireless charging is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
- Transmitter and Receiver Coils:
A transmitter coil in the charging pad generates an electromagnetic field when an electric current flows through it. When a device with a receiver coil is placed near the pad, the magnetic field induces a current in the receiver, which is converted to DC power and charges the battery.
- Inductive vs. Resonant Charging:
Inductive charging requires close contact between the charger and device, while resonant charging works over greater distances. In resonant charging, both coils are tuned to the same frequency, allowing more efficient energy transfer even when the device is slightly misaligned with the charger. - Qi Standard:
The Qi standard, widely adopted in smartphones, ensures interoperability and safety across devices. Other standards, like AirFuel, have also been developed but are less commonly implemented.
Wireless Charging
Technology and Applications
Wireless charging has expanded across various sectors, thanks to technological advancements:
- Consumer Electronics:
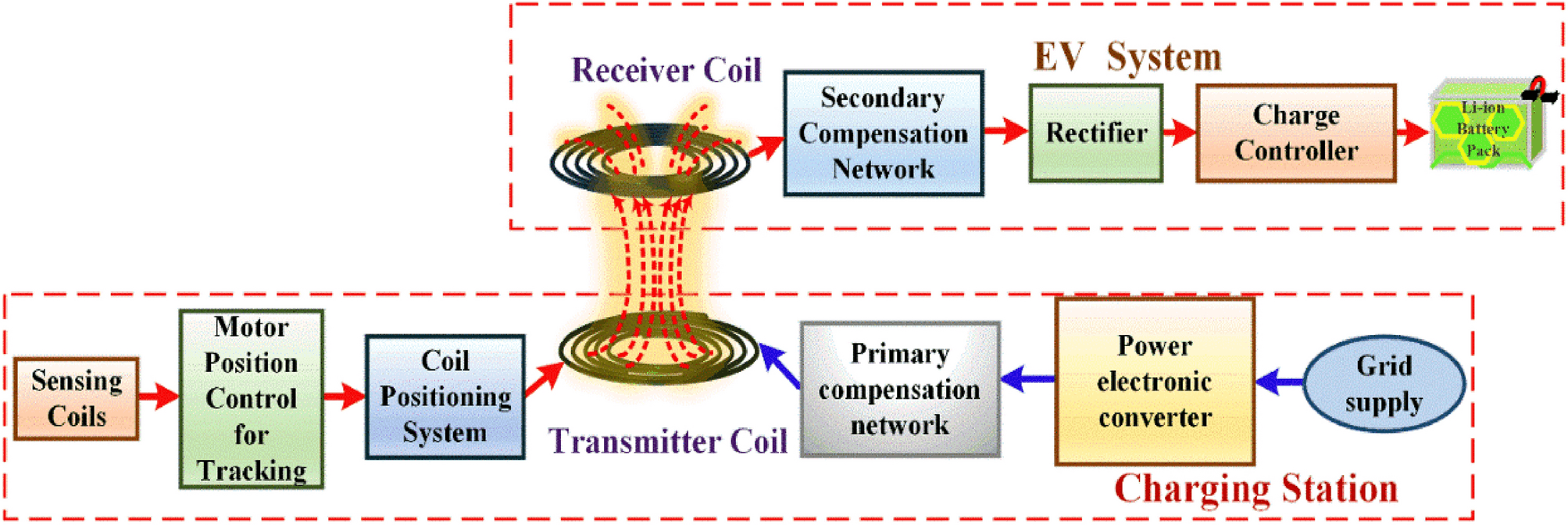
Smartphones, smartwatches, earbuds, and other small devices are commonly charged wirelessly, using Qi-certified pads. - Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Wireless charging pads embedded in parking spaces or garages offer convenience for EV owners. Some companies are exploring dynamic charging, where EVs charge while driving over embedded coils in the road. - Medical Devices:
Wireless charging for implantable medical devices reduces the need for external ports, minimizing infection risks and improving patient safety. - IoT and Smart Home:
Wireless power can support small IoT sensors, reducing maintenance for battery changes and creating more resilient, always-on systems in smart homes.
Leading Companies in
Wireless Charging
Several companies are leading the development of wireless charging technology:
- Apple:
Apple’s adoption of Qi charging for iPhones significantly boosted wireless charging’s popularity. The company also introduced MagSafe, a magnet-based system that aligns devices for optimal charging.
Wireless charger - Samsung: Samsung was an early adopter of wireless charging in its Galaxy series and has continued to support and expand wireless charging options across its devices.
- WiTricity: A pioneer in magnetic resonance technology, WiTricity focuses on EV wireless charging, aiming to transform charging infrastructure.
- Powermat: Known for its public charging pads in cafes and airports, Powermat provides wireless charging solutions that are compatible with multiple devices.
Benefits of
Wireless Charging
Wireless charging offers several advantages:
- Convenience:
No need forcables or physical connections. Simply placing a device on a pad is enough to start charging. - Durability:
Wireless charging reduces wear and tear on charging ports, increasing the longevity of devices. - Safety:
Eliminates therisk of electric shockfromexposed wires, and is increasingly safe for implanted devices. - Aesthetic and Practical:
Especially beneficial in public spaces, wireless charging can help reduce clutter and allow for integrated charging surfaces in furniture or vehicles.
Challenges of
Wireless Charging
Despite its benefits, wireless charging faces challenges:
- Efficiency:
Wireless charging is generally less efficient than wired charging, often resulting in slower charging times. - Heat Generation:
Wireless charging generates more heat, which can affect battery life and efficiency if not managed well. - Cost:
Implementing wireless charging systems, particularly for EVs and large devices, can be costly and infrastructure-intensive. - Interoperability:
Different standards can lead to compatibility issues, although the Qi standard has helped address this for many consumer devices.
The Future of
Wireless Charging
The future of wireless charging holds exciting possibilities, including:
- Mid-Range and Long-Distance Charging:
As resonant charging becomes more efficient, devices could charge from several feet away, allowing entire rooms to act as charging zones. Companies like Ossia and Energous are researching solutions for true wireless power transfer. - Dynamic EV Charging:
Roads embedded with wireless chargers could allow EVs to charge while in motion, eliminating range anxiety and reducing reliance on stationary charging stations. - Wireless Charging in Smart Cities:
Wireless charging for IoT devices in urban areas could support smart city infrastructure, from sensors and cameras to autonomous drones and robots. - Increased Efficiency:
Improving charging efficiency remains a top priority, with ongoing research into better materials, coil design, and thermal management to bring wireless charging closer to wired speeds.
Conclusion
Wireless charging technology is revolutionizing the way we power our devices, creating new opportunities for convenience, safety, and efficiency across multiple industries. As challenges around efficiency and cost are addressed, wireless charging is set to become a staple in our lives, potentially as ubiquitous as Wi-Fi. The innovations on the horizon promise a future where charging is as seamless as placing a device down, freeing us from cables and bringing us closer to a truly wireless world. 🙂
(Tick notification ![]() for more updates)
for more updates)