An Explainer on Apple’s Rise and Its Modern Monopoly Controversies
The Humble Beginnings:
Apple vs. IBM in the 1980s
-The 1984 Macintosh Launch
In 1984, Apple introduced the Macintosh, disrupting the computing market with a revolutionary ad aired during the Super Bowl. The commercial cast Apple as a brave insurgent defying the oppressive “Big Brother”—a symbol of IBM’s dominance. This bold narrative aligned Apple with the countercultural, creative, and rebellious spirit of the time.
-IBM: The Goliath of the Early Computing Era
IBM was the undisputed king of enterprise computing. Its machines filled offices and data centers around the world. Apple’s Mac, with its graphic user interface and mouse, broke from the command-line norm and offered a more human-friendly approach to computing—marking a pivotal shift in user interaction.
The Irony of Time:
Apple Becomes the New IBM?
-Apple’s Meteoric Rise
From struggling startup to corporate behemoth, Apple’s evolution is a story of innovation, branding, and strategic ecosystem development. Steve Jobs’ return in 1997 ushered in a renaissance, culminating in the launch of the iPod (2001), iPhone (2007), iPad (2010), and Apple Watch (2015). These products, coupled with tightly integrated services, drove Apple to the top of the tech hierarchy.
-Dominance in the Mobile Ecosystem
Today, Apple’s influence in mobile technology is unrivaled. The iPhone generates more revenue than many Fortune 500 companies. With iOS, Apple controls everything from software to distribution—offering consistency and security, but also stoking accusations of monopoly due to its restrictions on developers and users alike.
Apple’s Walled Garden:
Control Over Hardware and Software
-The App Store as a Toll Booth
Apple takes a cut—typically 30%, reduced to 15% for smaller developers—on most App Store transactions. This business model has generated billions, but has also drawn fire from developers who argue they are forced into an uneven relationship with Apple’s platform.
-No Sideloading Allowed
Apple prohibits sideloading on iOS, unlike Android. This means all app installations must go through the App Store, giving Apple complete control over app distribution, review, pricing rules, and content moderation.
Tight Integration:
Hardware and Software Harmony
Apple’s seamless user experience is often praised. However, the harmony is maintained by locking users into an ecosystem. AirPods, the Apple Watch, iCloud, and iMessage function best—or only—with Apple hardware, discouraging cross-platform flexibility.
-The Lightning Port Controversy
Apple’s insistence on the proprietary Lightning connector for iPhones, despite widespread adoption of USB-C, has been criticized as a tactic to sell more accessories and maintain proprietary control. New EU laws may soon force universal port adoption.
Epic Games vs. Apple:
A Modern-Day 1984
-Fortnite’s Banishment
In 2020, Epic Games pushed back against Apple’s in-app payment requirements by introducing an alternative payment method in Fortnite. Apple swiftly removed Fortnite from the App Store for violating guidelines, triggering a legal and cultural firestorm.
Epic’s Counterattack:
“Nineteen Eighty-Fortnite”
Epic parodied Apple’s famous 1984 commercial, portraying Apple as the new tech overlord. The video, viewed millions of times, was a powerful PR move that reframed Apple’s image in the public eye and ignited debate on platform control and developer rights.
IBM became a monopoly by Apple’s criticism
Apple became a monopoly by Epic Game’s criticism
Monopolistic Behavior or Just Smart Business?
-Critics: Apple Stifles Innovation
Detractors argue that Apple’s rigid ecosystem and App Store restrictions hurt competition, limit consumer choice, and squeeze developers. Critics include prominent app creators, regulators, and former Apple allies who believe the company has abandoned its original ethos.
-Apple’s Defense: Quality, Security, and Privacy
Apple counters these criticisms by citing its commitment to privacy and security. The company insists that maintaining tight control ensures a safe, seamless, and high-quality user experience.
-The “Gatekeeper” Label
Apple has been branded a “gatekeeper” under new regulatory frameworks, particularly in the EU. This label highlights its significant influence over access to a major portion of mobile commerce, communications, and entertainment.

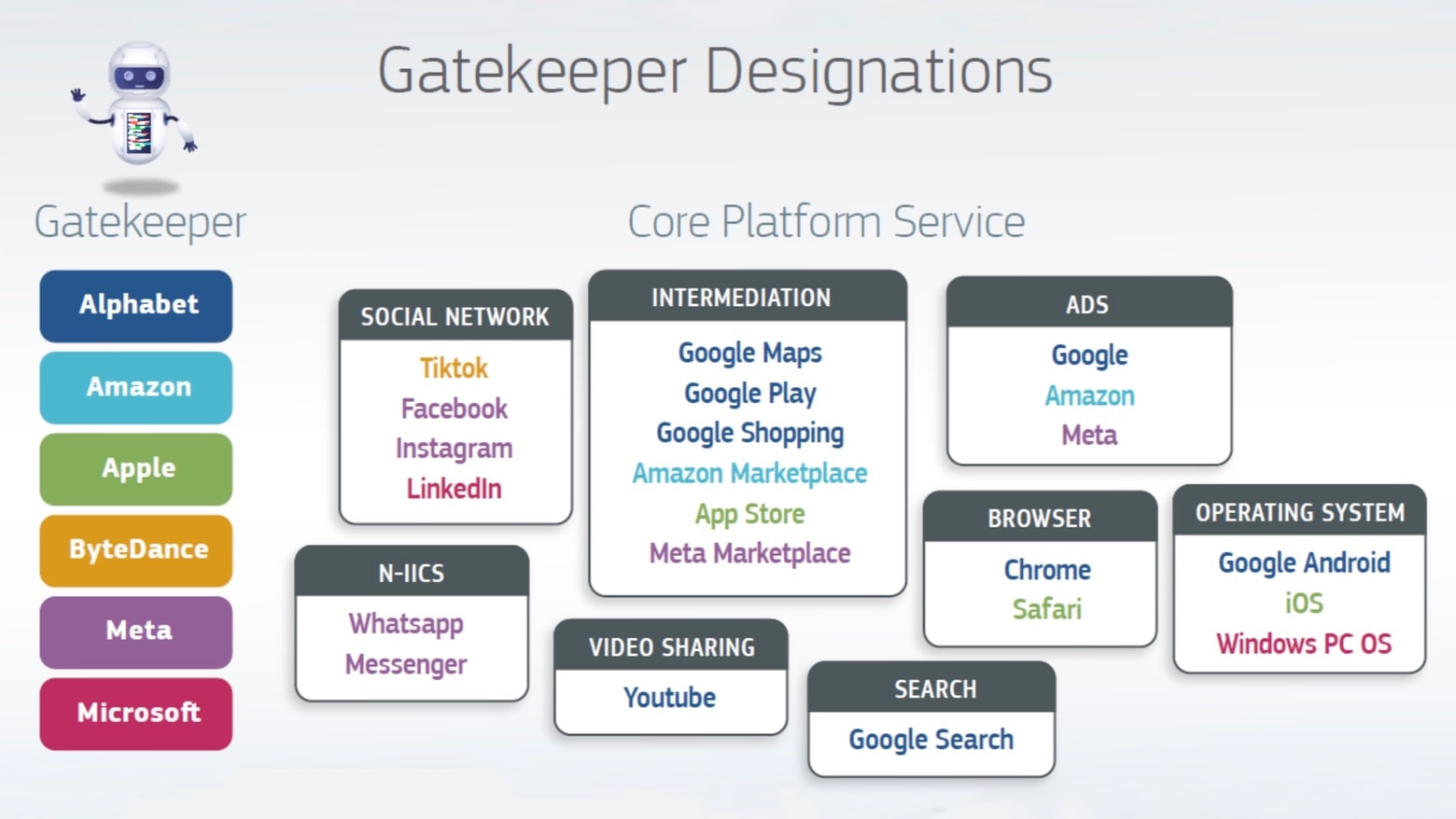
Global Antitrust Investigations
-The EU Steps In
The European Commission has pursued multiple investigations into Apple’s App Store practices, including Spotify’s antitrust complaint. Apple is accused of using its gatekeeper status to favor Apple Music over Spotify and impose unfair terms on developers.
-U.S. Scrutiny
The U.S. Department of Justice is investigating Apple’s control over app distribution and digital commerce. State attorneys general from numerous states have joined the effort, focusing on whether Apple’s practices violate antitrust laws.
-Japan and South Korea Join the Fight
In Asia, Apple faces growing pressure. South Korea has passed laws requiring Apple and Google to allow alternative payment systems, while Japan is considering similar action. The global nature of these inquiries indicates a growing consensus around curbing Big Tech’s power.
Apple vs. Epic:
The Courtroom Battle
–Key Issues in the Lawsuit–
The legal battle raised foundational questions:
- Should Apple be allowed to mandate its payment system?
- Is Apple’s control over iOS anti-competitive?
- What rights should developers have on closed platforms?
-The Verdicts So Far
The case resulted in a partial win for both sides. Apple was ordered to allow developers to link to outside payment options. However, the court ruled that Apple was not a monopoly under current U.S. law. The decision is under appeal.

-What This Means for Developers
The lawsuit sparked broader discussions about platform fairness, catalyzing efforts by developers and regulators to reevaluate the status quo. Many developers feel more empowered to speak out, knowing their concerns are being acknowledged in public forums. (But only on US)
Other Companies That Have Challenged Apple
-Spotify’s Complaint
Spotify alleges Apple’s 30% fee and App Store rules unfairly advantage Apple Music. It also claims Apple limits user communication and restricts pricing flexibility, creating an uneven playing field.
-Basecamp’s “Hey” App Battle
The creators of “Hey,” a premium email app, clashed with Apple over in-app payments. Apple initially blocked the app from updates until it complied. The incident sparked developer outrage and renewed calls for reform.
-Tile vs. Apple AirTag
Tile, a Bluetooth tracking device company, claims Apple disadvantaged them by introducing AirTags with deeper iOS integration. Apple’s system-level access gives AirTags features that third-party competitors cannot match.
The Double Standard Debate
-Apple on Mac vs. iPhone
On Macs, users can install apps from any source, but on iPhones, Apple enforces total control. Critics argue this inconsistency undermines Apple’s justification that control is necessary for security.
-Consumer Choice vs. Company Control
While many users appreciate Apple’s simplicity, others want more freedom. The core issue: Should a consumer’s ability to modify or customize their device be limited by a manufacturer?
Developers Speak Out
-Coalition for App Fairness
Formed in 2020, this alliance includes Epic, Spotify, Basecamp, and others. It advocates for platform neutrality, transparent rules, and the right to use alternative payment systems.


-Voices from the Indie Dev Community
Independent developers have voiced frustration over vague App Store guidelines, arbitrary rejections, and a lack of negotiation power. For many small businesses, Apple’s rules can make or break their product.
Apple’s Ecosystem as a Lock-In Strategy
-The Power of iCloud, iMessage, and FaceTime
Apple’s ecosystem thrives on convenience. Services like iMessage and FaceTime work only with Apple devices, creating powerful incentives to stay within the Apple environment.![]()
-Cross-Device Features:
A Blessing and a Barrier
Features such as AirDrop, Handoff, Universal Clipboard, and Continuity Camera exemplify the strength of Apple’s integration. Yet, they also make it harder to leave the ecosystem without losing functionality.
-Switching Costs and User Stickiness
Switching from iOS to Android can be daunting due to data migration, app purchases, and service compatibility. Apple benefits from high user retention enabled by these barriers.
Looking Ahead:
Will Regulation Break Apple’s Grip?
-The Digital Markets Act (DMA)
The EU’s DMA aims to prevent Big Tech from abusing gatekeeper positions. It may require Apple to open its platform to alternative app stores and allow sideloading, potentially transforming the iOS experience.
-U.S. Legislative Efforts
U.S. lawmakers have introduced bills such as the Open App Markets Act. These laws seek to ensure fairness by requiring access to third-party payment systems and preventing platform self-preferencing.
-Will Apple Preemptively Open Its Platform?
Facing mounting pressure, Apple may introduce reforms voluntarily. For instance, Apple recently allowed alternative app stores in the EU in response to regulation—possibly signaling a shift in strategy.
Conclusion:
A New Kind of Monopoly?
Apple’s transformation from revolutionary disruptor to dominant incumbent has invited comparisons to IBM’s past. As Apple tightens its grip on hardware, software, and services, the debate intensifies: is Apple simply protecting its users, or exploiting its dominance?
While the answers remain complex, one thing is clear: the global conversation around Apple’s role in the digital economy is far from over. Developers, regulators, and users alike are questioning what digital freedom means—and who gets to define it.
Bonus:
A Timeline of Key Events in Apple’s Antitrust History
- 1984: Apple’s “1984” ad vs. IBM
- 2001: iPod launch
- 2007: iPhone launch
- 2010: App Store becomes dominant
- 2019: Spotify files EU complaint
- 2020: Epic Games sues Apple
- 2021: Coalition for App Fairness gains traction
- 2022: Global regulatory attention intensifies
- 2024: EU’s DMA enforcement begins
References and Further Reading
- U.S. vs. Apple court documents
- EU Commission press releases
- Epic Games legal filings
- Coalition for App Fairness
- Tech policy analysis from the Electronic Frontier Foundation and Public Knowledge
- News coverage from The Verge, Bloomberg, Wired, and The Wall Street Journal
(Click notification ![]() for more updates)
for more updates)
By: V.Harishram
”Stay true, bring facts to you”

