Neuralink was launched in 2016 and was first publicly reported in March 2017.It was founded by Elon Musk and a team of seven scientists and engineers (Max Hodak, Benjamin Rapoport, Dongjin Seo, Paul Merolla, Philip Sabes, Tim Gardner, Tim Hanson, and Vanessa Tolosa).The implantation of the device, called “the Link,” represents a leap forward in the realm of BCIs, which record and decode brain activity, that may allow for new innovations in health care, communication, and cognitive abilities.
–What is Neuralink chip?–
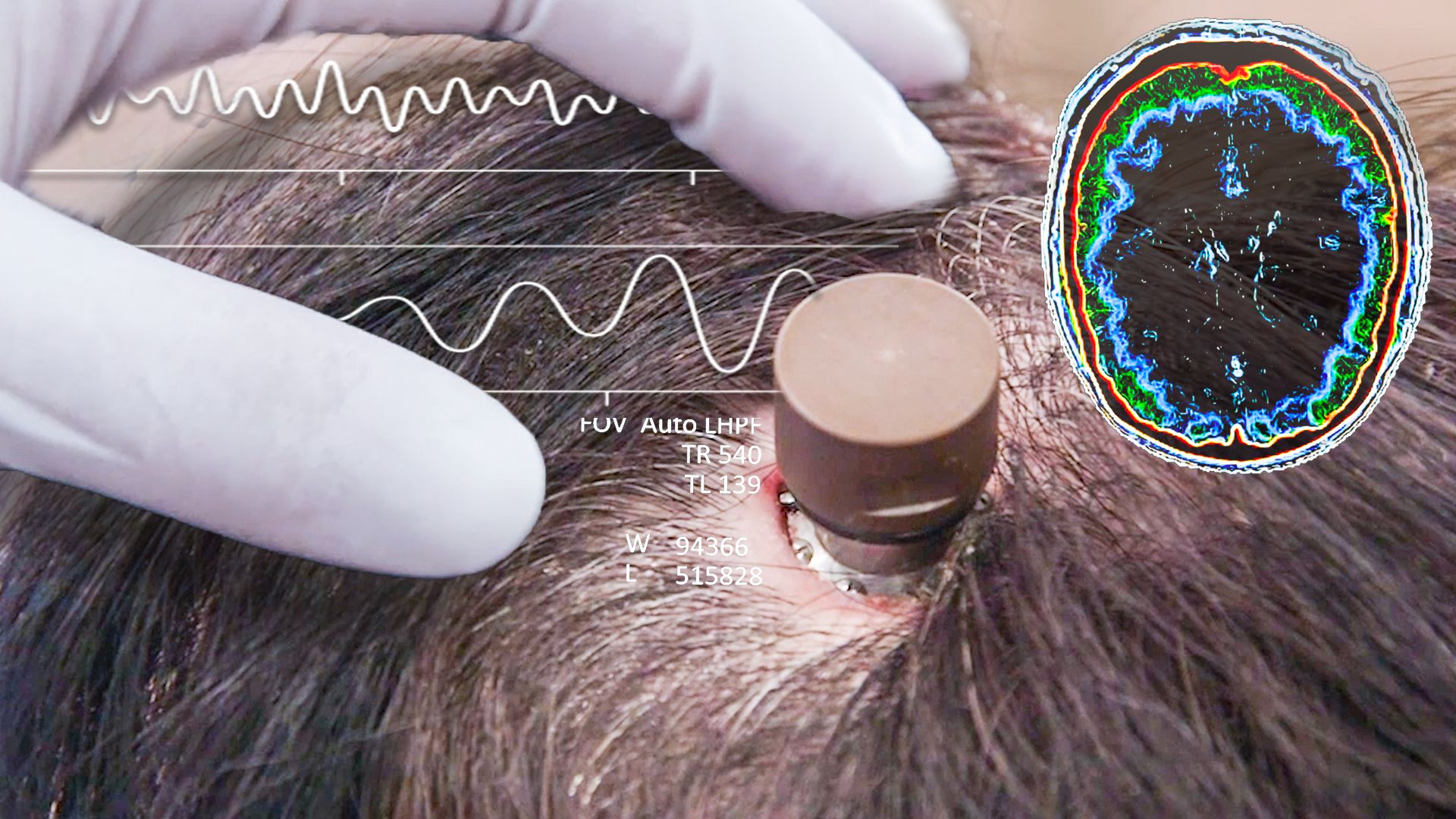
This coin-sized brain chip is surgically embedded under the skull, where it receives information from neural threads that fan out into different sections of a subject’s brain in control of motor skills. Each wire contains sensors capable of recording and emitting electrical currents that are “so fine that they can’t be inserted by the human hand,” according to Neuralink’s website.It could be used to control exoskeletons and prosthetics That’s why Neuralink has built a neurosurgical robot that’s designed to become fully automated.The company is also developing an app that would allow a person to manipulate a keyboard and mouse using only their mind.“Neuralink is really at the vanguard of creating the commercialized, scalable versions of what has been pioneered in academia,” said Sumner Norman, a scientist at nonprofit startup Convergent Research and former chief brain-computer interface scientist at software firm AE Studio.“There’s been decades of academic research to push this [field] as far as it can go,” he said, “but ultimately, it becomes a very expensive space to develop.”
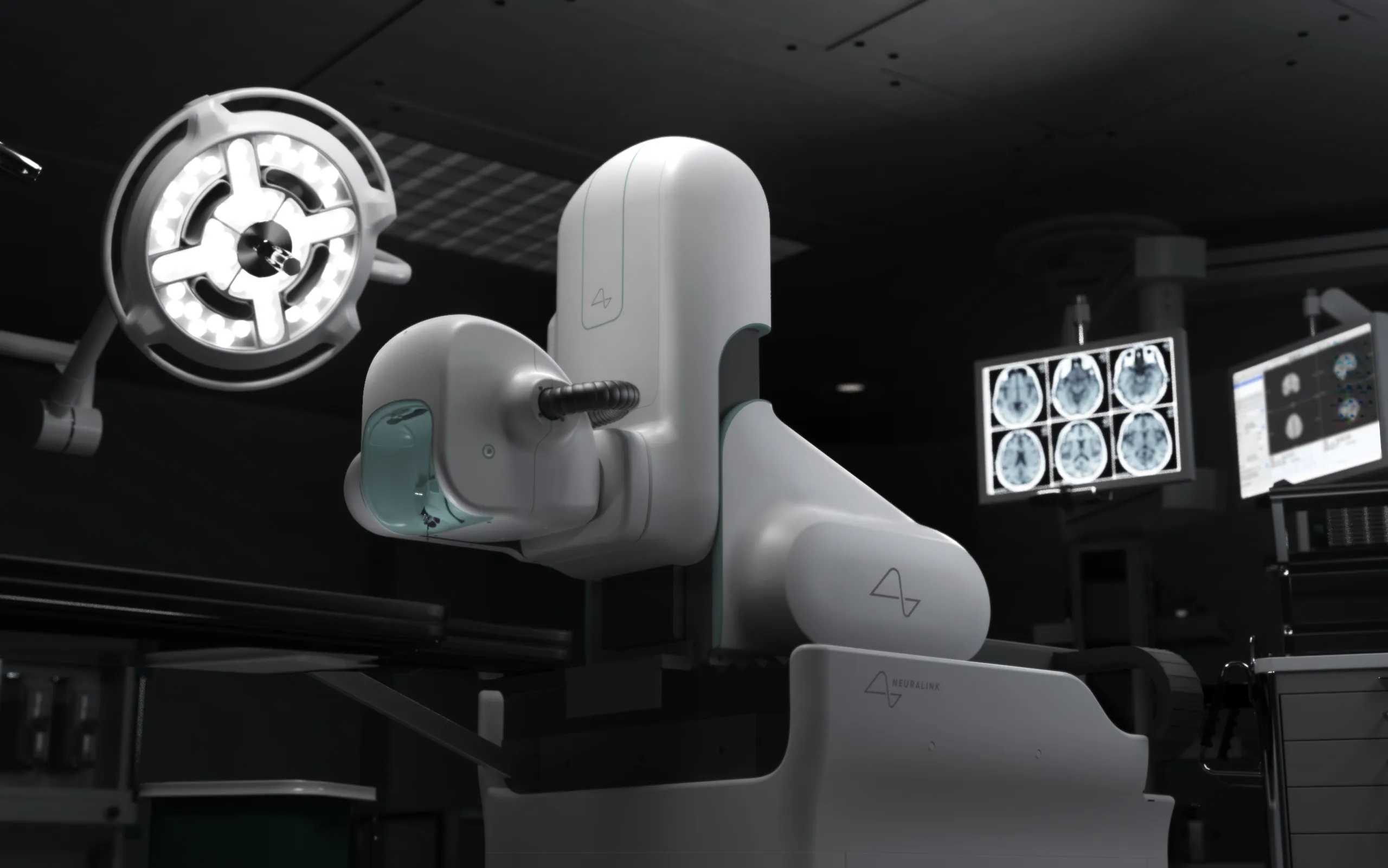
–Neuralink Surgical Robot —
The study uses a robot to surgically place a brain-computer interface (BCI) implant in a region of the brain that controls the intention to move. Neuralink just demonstrated its surgical robot for the first time, showing the world during a livestreamed event how the bot could swiftly and precisely insert electrode-packed threads into a dummy brain.On November 30, Musk hosted another “show and tell” livestream.This time, the company gave viewers their first look at the Neuralink robot in action, demonstrating how it could insert 64 threads containing 16 electrodes each into a gelatinous “brain proxy” of a dummy patient over the course of about 15 minutes.
–Human test —
Neuralink received FDA approval for human clinical trials in May 2023.In September 2023, Neuralink opened up its first human trials. It recruited people with quadriplegia (a symptom of paralysis that affects all a person’s limbs and body from the neck down) due to cervical spinal cord injury or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis under an investigational device exemption by the FDA.On January 29, 2024, Musk said that Neuralink had successfully implanted a brain computer interface – BCI (allow you to control an application or a device using only your mind).Device the company named Telepathy in a human on the day prior, and that the patient was recovering from the surgery.
–Possible problems with it–
- Brain injury or infection
- Physical side effects like bleeding, headaches, nausea or seizures
- Psychological side effects like mood changes
- Allergic reaction to implanted materials
- Movement of implanted threads and wires to other parts of the brain
- Cybersecurity, hacking and privacy vulnerabilities
- Unknown long-term effects of use
–Conclusion —
If the technology proves successful, the company hopes to create direct brain-to-computer interfaces that connect a person’s thoughts to digital devices. Musk’s long-term vision is to combine human consciousness with artificial intelligence, a claim that has drawn considerable skepticism from scientists. In the medical realm, Neuralink could offer new avenues for treating neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease. It could be used to control exoskeletons and prosthetics that could restore movement in individuals with paralysis or amputations. The technology also opens doors to human enhancement through memory augmentation and enhanced cognitive abilities.
Article written by V.Harishram.




It’s easy to read.But it was very old one but this will be informative to more peoples who doesn’t know about this much.And I suggest to add photo about chess playing through this.
Magnificent beat I would like to apprentice while you amend your site how can i subscribe for a blog web site The account helped me a acceptable deal I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear idea