In an age where data generation is expanding exponentially, traditional storage systems are struggling to keep up. Hard drives, cloud servers, and magnetic tapes are nearing their physical and practical limitations. Meanwhile, researchers are turning to DNA—the molecule that carries genetic information in all living things—as an unlikely but incredibly promising solution for data storage. DNA’s inherent density, durability, and abundance make it an excellent candidate for storing digital information, opening up a revolutionary new pathway for the future of data storage.
What is DNA Data Storage?
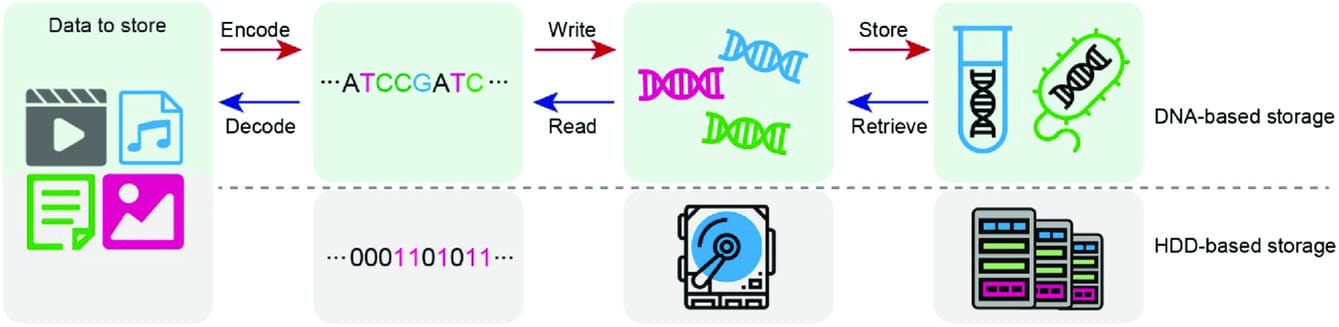
DNA data storage is a method of storing digital information in synthetic DNA molecules by converting binary data (1s and 0s) into DNA’s four nucleotide bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). DNA’s molecular structure can be used to represent digital data in an ultra-compact form. The process requires encoding binary data into sequences of these bases, synthesizing the corresponding DNA.strands, and then storing them in a stable environment.
Unlike silicon or magnetic-based storage systems, DNA has a unique capability: it can remain stable for thousands of years, making it a compelling alternative for long-term data archiving.
The Science Behind
DNA as a Storage Medium
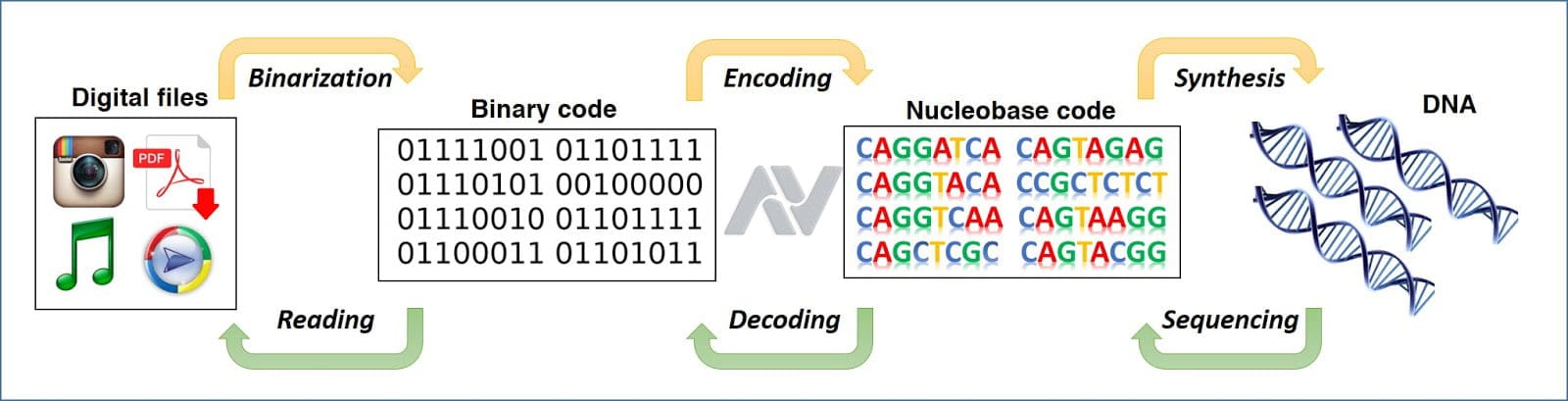
At the core of DNA data storage is a process of converting binary data into DNA sequences, which can be thought of as a biological version of computer encoding. Binary sequences of 1s and 0s are transformed into combinations of the four nucleotides. For instance, a coding scheme might pair binary numbers with specific DNA bases, with “00” representing adenine (A), “01” as thymine (T), “10” as cytosine (C), and “11” as guanine (G).
Scientists use sophisticated encoding algorithms to ensure data accuracy, then synthesize these DNA sequences in the lab. DNA synthesis machines are used to construct the physical DNA strands, which can then be stored for future reading. When it’s time to retrieve the data, scientists use DNA sequencing technology to decode the stored information, transforming the nucleotide sequences back into binary data that can be read by computers.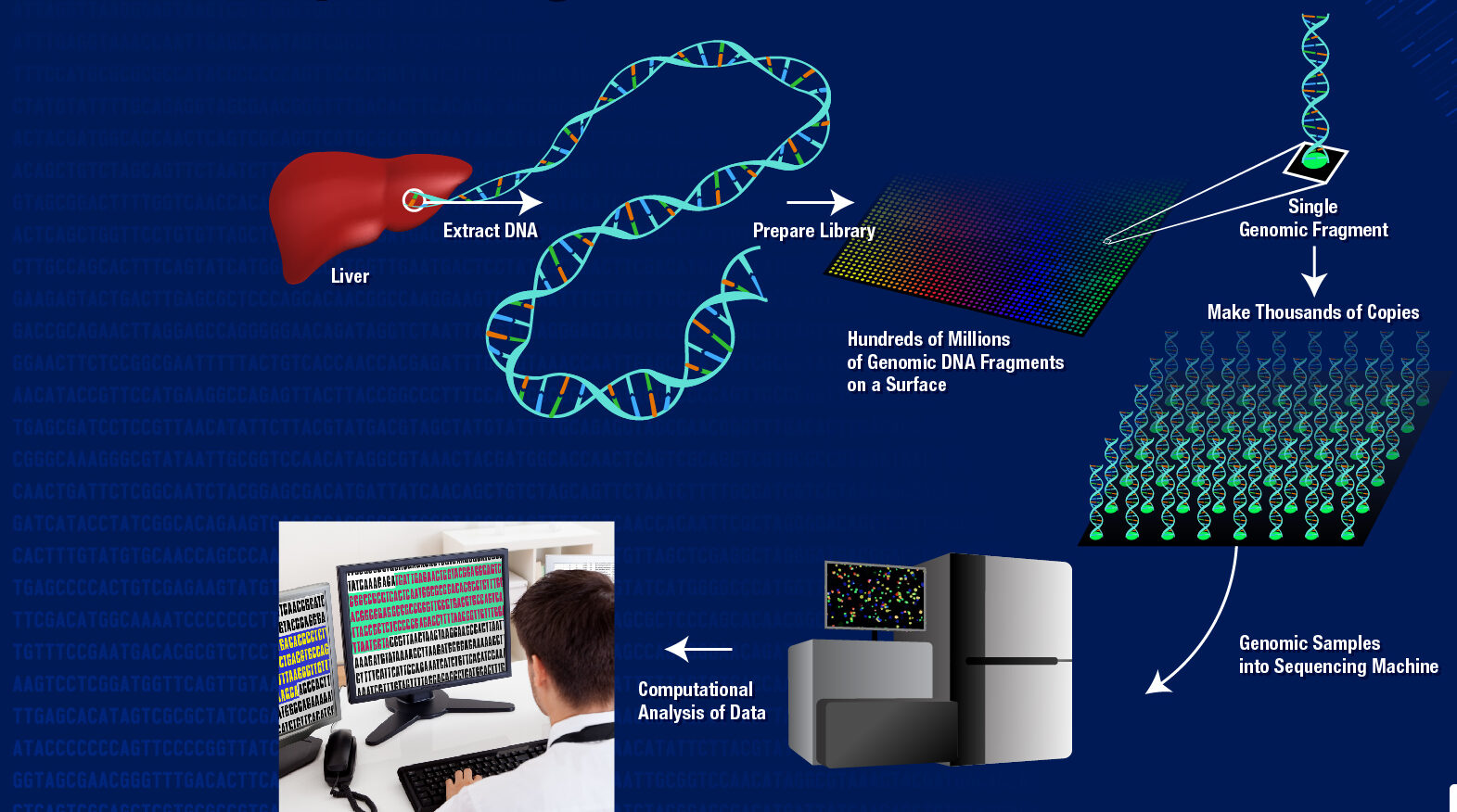
The Technology:
How Does DNA Data Storage Work?
The DNA data storage process consists of several technical steps:
- Data Encoding:
First, digital information is encoded into DNA sequences using binary-to-nucleotide conversion algorithms. These algorithms are designed to create stable DNA strands while avoiding repetitive sequences that couldincrease error rates.
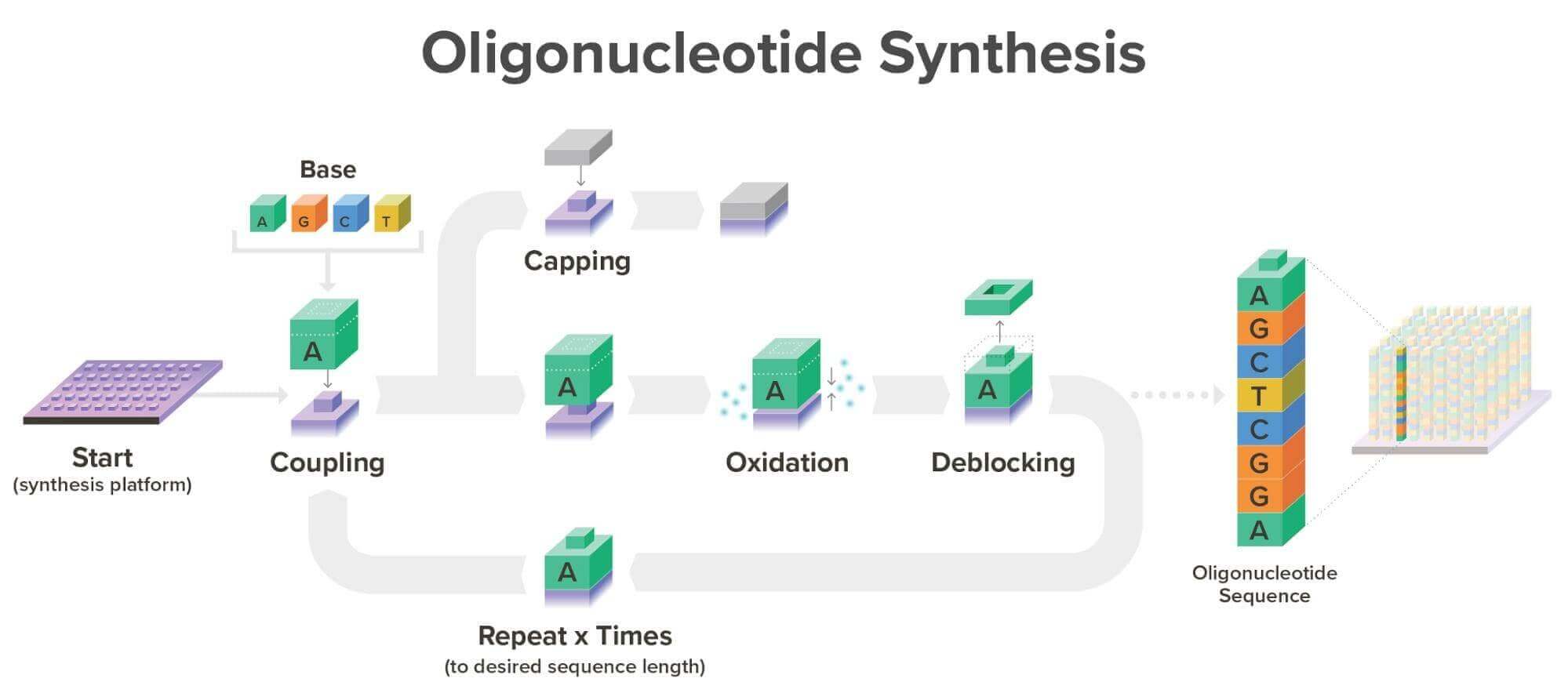
- DNA Synthesis:
Once the data is encoded, synthetic biology techniques are used to manufacture DNA strands that correspond to the encoded sequence.
- Storage:
The synthesized DNA is then stored in a controlled environment, often freeze-dried in microtubes. This preserves the DNA for long-term use, as it remains stable at room temperature for centuries or even millennia. - Data Retrieval:
To access the stored data, the DNA is sequenced, meaning its base sequence is read back and decoded into binary format. This data is then converted back into readable digital information.
While DNA synthesis and sequencing are currently costly and slow, ongoing research is working to bring down costs and improve the efficiency of the process.
Companies Leading the Way
Several prominent companies are pioneering advancements in DNA data storage:
- Microsoft:
Microsoft Research has been actively exploring DNA storage for years. The company has partnered with the University of Washington to develop more efficient encoding and retrieval techniques and recently demonstrated a DNA-based storage system prototype.
first fully automated DNA data storage – https://news.microsoft.com/source/features/innovation/hello-data-dna-storage/ - Twist Bioscience:
Specializing in synthetic biology, Twist Bioscience produces DNA at a large scale, positioning itself as a crucial supplier for DNA data storage. The company is working on reducing DNA synthesis costs and increasing the efficiency of the storage process.
https://www.twistbioscience.com/ - Catalog Technologies:
Catalog uses a unique approach to DNA storage, relying on specialized encoding schemes to store large datasets. The company aims to make DNA data storage more practical for large enterprises, focusing on scalable, high-density data storage solutions.
Benefits of
DNA Data Storage
DNA data storage offers several advantages that set it apart from traditional storage solutions:
- High Density:
DNA can store enormous amounts of data in a tiny volume—approximately 215 petabytes per gram. This is orders of magnitude beyond the capacity of traditional storage media. - Longevity:
Unlikemagnetic tapes or hard drives, DNA can remain stable for thousands of years if kept in the right conditions. This makes it ideal for archival storage. - Environmental Sustainability:
DNA requires no electricity for long-term storage, reducing its environmental impact compared to data centers, which need constant power and cooling.
Disadvantages and Challenges
Despite its promise, DNA data storage faces several obstacles:
- Cost:
Currently, the cost of synthesizing and sequencing DNA is prohibitively high. Storing a single megabyte of data can cost thousands of dollars, making it impractical for mainstream use at this time. - Speed:
Writing and reading data in DNA is slow compared to traditional storage media. DNA synthesis is a time-consuming process, and reading the data back requires DNA sequencing, which can also be lengthy. - Error Rates:
Errors can arise during both DNA synthesis and sequencing, requiring complex error-correction mechanisms to ensure data integrity. Researchers are continually developing new methods to improve accuracy.
The Future of
DNA Data Storage
DNA data storage is still in its infancy, but the potential applications are vast. With ongoing research and technological advancements, DNA data storage could eventually become a viable option for long-term data preservation, especially for institutions that require archival storage.
Over the coming years, as costs for DNA synthesis and sequencing decrease, we may see DNA data storage become a mainstream option. Researchers are already exploring ways to automate DNA synthesis, further reducing costs and improving speed. Advances in sequencing technologies are also improving data retrieval speeds, making DNA storage more accessible.
Several governments and organizations are interested in DNA storage for global knowledge preservation. The possibility of storing the entirety of human knowledge in a few grams of DNA represents an invaluable tool for preserving information for future generations.
Conclusion
DNA data storage is a groundbreaking solution with the potential to address modern storage challenges. Its unparalleled data density, durability, and sustainability make it an exciting area of research and development. Although the technology is currently limited by high costs and technical hurdles, advancements in synthetic biology and sequencing may soon make DNA storage a reality for critical applications.
As we face an ever-growing need for data storage, DNA offers a vision of a future where data can be preserved securely and efficiently for centuries. DNA data storage is not just a technological innovation; it represents a powerful bridge between biology and digital information, merging the essence of life with the preservation of knowledge.
(Click notification ![]() for more updates)
for more updates)