In recent years, eSIM technology (Embedded Subscriber Identity Module) has emerged as a groundbreaking advancement in mobile connectivity. By removing the need for traditional, physical SIM cards, eSIM technology simplifies the way we connect devices to mobile networks, creating opportunities for more versatile, flexible, and user-friendly connectivity solutions. In this article, we’ll explore the details of eSIM technology, including its history, functioning, benefits, challenges, and what lies ahead.
What is eSIM Technology?
An eSIM, or embedded SIM, is a digital version of the physical SIM card that allows users to connect to a mobile network without inserting a physical SIM into their device. Embedded within the device’s hardware, an eSIM is reprogrammable and can store multiple carrier profiles, enabling users to switch carriers or plans remotely. This capability offers significant advantages in terms of flexibility and device design, especially as the need for cross-border and multi-device connectivity grows.
History of eSIM Technology
The idea of a SIM card emerged in 1991 when it was developed as a key enabler for digital cellular networks, but the design and functionality remained mostly the same for years. By the early 2010s, the rise in mobile devices and connected Internet of Things (IoT) led the industry to rethink SIM technology. In 2016, the GSMA (Global System for Mobile Communications) standardized the first specifications for eSIM, paving the way for major mobile device manufacturers, such as Apple and Samsung, to adopt it in their products. Today, eSIM has become increasingly common in smartphones, smartwatches, laptops, and IoT devices.
How Does eSIM Technology Work?
eSIM technology operates through an embedded microchip in a device’s motherboard, which is activated through remote provisioning by a carrier. Users can download carrier profiles by scanning QR codes or using carrier apps, allowing the eSIM to connect to the selected network without physically swapping cards. eSIM profiles can store multiple carriers, so switching between plans or roaming networks is easy and instantaneous. This flexibility makes it ideal for global travelers and IoT applications, where seamless switching is beneficial.
Companies Leading the eSIM Market
Several companies are leading the charge in eSIM technology adoption and innovation. Key players include:
- Apple:
As one of the earliest adopters, Apple introduced eSIM in its iPhone XS series and has expanded eSIM compatibility in subsequent models. - Samsung:
Samsung supports eSIM in its Galaxy line, especially on models like the Galaxy S20 and newer. - Google:
Google also adopted eSIM in its Pixel lineup, providing a seamless option for users to switch carriers. - Qualcomm:
Known for manufacturing chips, Qualcomm supports eSIM with its processors that cater to IoT, wearable, and mobile device industries. - Other Carriers and Startups:
Major telecom providers and emerging startups are offering services to support eSIM integration and provisioning.
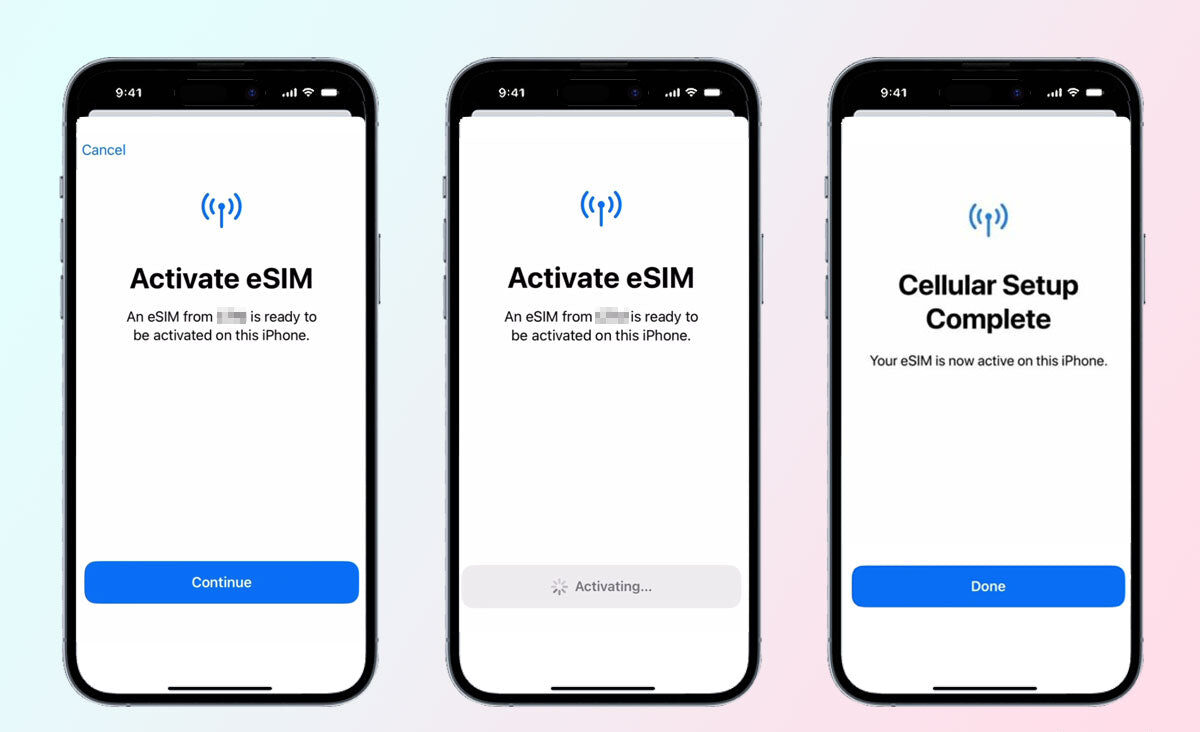
Steps to Activate an eSIM
- Check Device Compatibility:
Verify that the device supports eSIM functionality. - Choose a Carrier:
Select a carrier that offers eSIM plans. This is becoming widely available but may still vary by country and provider. - Download the Profile:
Using the carrier’s app or a QR code, download the eSIM profile to your device. - Activate:
After download, activate the eSIM profile, connecting to the carrier network without needing to insert a physical SIM card. - Switch and Manage:
Users can switch between profiles or activate a new one as needed, making it easier to handle multiple plans.
Benefits of eSIM Technology
- Convenience:
With eSIM, users can switch carriers withoutphysically changing SIM cards, providing flexibility for international travel and multi-network support. - Smaller Devices:
eSIM enables manufacturers to save space within devices, which can be used to improve battery life, add more features, or create more compact designs. - Environmentally Friendly:
Reducing the need for physical SIM cards cuts down on plastic waste, aligning with sustainability goals. - Enhanced IoT Connectivity:
eSIM makes IoT device deployment simpler and more scalable, allowing for smoother integration and management across industries.
Challenges Facing eSIM Technology
- Limited Carrier Support:
While many carriers support eSIM, not all providers offer this service, and coverage may vary by region. - Security Concerns:
Remote provisioning of eSIM profiles can raise security issues, making it crucial to implement robust security measures. - Device Compatibility:
Not all devices support eSIM, and many users still rely on traditional SIM cards. - User Familiarity:
Some users may find the technology challenging to understand, as it requires managing profiles digitally.
Conclusion
eSIM technology represents a pivotal shift in connectivity, offering a glimpse into a future where device connectivity is more flexible, streamlined, and user-centric. With the backing of major device manufacturers and growing carrier support, eSIM adoption is set to accelerate, especially as more devices become interconnected across global networks. While challenges remain in terms of adoption and security, the benefits far outweigh these issues, making eSIM technology a promising advancement in the telecommunications industry.
(Click notification ![]() for more updates)
for more updates)
Artical was written by V.Harishram