Holographic displays are rapidly advancing and pushing the boundaries of visual technology. From futuristic films to practical applications in medicine, education, and entertainment, holographic displays are transforming our digital interaction by creating immersive, 3D visuals without the need for special glasses. This article explores what holographic displays are, the technology behind them, their applications, industry leaders, challenges, and the future potential of this groundbreaking technology.
What are Holographic Displays?
Holographic displays create three-dimensional (3D) images by projecting light in a way that produces the illusion of depth. Unlike 2D screens, which display images on a flat surface, holographic displays appear as floating, lifelike images that can be viewed from different angles. These displays provide a more immersive experience and can be used in a range of applications, from gaming and entertainment to healthcare and education.
The Technology Behind
Holographic Displays
Holographic displays rely on advanced technologies to generate realistic 3D images:
- Laser Interference:
This method uses laser light to record interference patterns on a surface, capturing the light’s shape and intensity. When light is projected through or reflected off this surface, it reconstructs the image in 3D. - Light Field Displays:
These displays capture light from various angles and reconstruct it in a way that allows viewers to perceive depth and parallax (where objects in the background appear to move slower than those in the foreground). - Spatial Light Modulators (SLMs):
SLMs are used to manipulate light in real-time, allowing dynamic 3D images to be created and updated as users interact with the display.
How Holographic Displays Work?
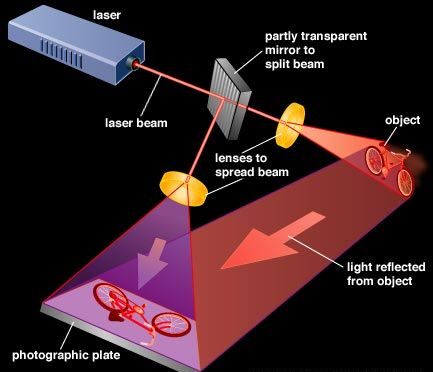
Holographic displays work by encoding visual information in light waves to create a three-dimensional representation. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Recording:
A laser beam is split into two parts: a reference beam and an object beam. The object beam reflects off the object to be displayed, while the reference beam remains unaltered. - Interference Pattern:
When the object and reference beams meet on a recording medium, they create an interference pattern, which captures the 3D properties of the object. - Reconstruction:
To view the hologram, light is projected onto the interference pattern, creating a reconstructed 3D image. Viewers see a lifelike representation with depth, allowing them to perceive details as though they were looking at the real object.
Leading Companies in
Holographic Displays
Several companies are at the forefront of developing holographic display technology:
- Looking Glass Factory:
This company creates high-quality holographic displays for 3D modeling, design, and even interactive 3D content.(https://lookingglassfactory.com/) - VividQ:
A leader in computer-generated holography, VividQ specializes in holographic displays for automotive and consumer electronics.
(https://www.vividq.com/) - Realfiction:
Known for its large-scale holographic displays, Realfiction focuses on applications in advertising and retail, providing a visually impactful way to showcase products.
(https://www.realfiction.com/) - Leia Inc.:
Leia offers holographic displays for mobile devices, providing immersive 3D visuals for smartphones and tablets.
(https://leiadisplay.com/)
Applications of Holographic Displays
1. Medical Imaging and Healthcare
Holography allows doctors to view 3D images of organs, tissues, or bones in real time. Surgeons, for example, can use holographic displays to plan and perform complex procedures with enhanced precision.
2. Education and Training
Holographic displays provide students with interactive, 3D visuals that enhance learning experiences in subjects like biology, physics, and history. Vocational training, such as medical or engineering simulations, benefits greatly from these hands-on holographic representations.
3. Entertainment and Gaming
Holography offers a new level of immersion in gaming and entertainment, with life-like characters and worlds that can exist in users’ physical space. In concerts, holograms allow virtual performances, bringing artists and events to audiences worldwide.
4. Retail and Advertising
Retailers use holographic displays to engage customers with interactive product demonstrations, enabling them to see, rotate, and even interact with 3D product representations.
5. Teleconferencing and Collaboration
Holographic teleconferencing allows participants to appear as life-size holograms, improving remote communication by adding a more lifelike presence to virtual meetings.
Challenges in
Holographic Display Technology
While the potential of holographic displays is immense, several technical and practical challenges remain:
- Computational Demand:
Rendering high-quality, dynamic holograms requires significant computational power, particularly for real-time applications. - Storage Requirements:
The vast amount of data needed to store and render 3D holographic images poses storage challenges, especially for high-resolution images. - Cost:
Holographic technology, especially for large displays, remains expensive to produce, limiting its availability for consumer markets. - Display Brightness and Contrast:
Holograms require precise control of light, and achieving high brightness and contrast can be difficult, especially in environments with ambient light.
The Future of
Holographic Displays
The future of holographic displays looks promising, with advances in AI, machine learning, and optical technology expected to drive further innovation. Improvements in quantum dot technology and light field manipulation will enable more affordable, high-resolution displays. Additionally, the integration of holography with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) could lead to more immersive and interactive experiences in various fields.
Consumer-level holographic displays are also on the horizon, as companies work to make the technology affordable for everyday use. This could lead to applications like holographic smartphones, home entertainment systems, and even holographic social media.
Conclusion
Holographic displays represent a major leap forward in visual technology, offering lifelike, immersive experiences across various industries. While challenges exist, advancements in technology are rapidly addressing these limitations. As holography becomes more accessible and affordable, it has the potential to revolutionize how we interact with digital information, making virtual experiences indistinguishable from reality. The future of holographic displays is bright, bringing us closer to a world where 3D holograms are part of our daily lives.
(Click notification ![]() for more updates)
for more updates)
Artical was written by V.Harishram