Introduction

In our interconnected world, language translation is essential, whether for international business, travel, or cross-cultural communication. Real-time language translation devices have emerged as a groundbreaking solution, enabling people to overcome language barriers instantly. Powered by advanced AI and natural language processing, these devices translate spoken or written words in real time, facilitating seamless conversations between speakers of different languages. This technology is revolutionizing how we communicate, bridging gaps between cultures and bringing the world closer together.
History of
Real-Time Language Translation Devices
The concept of machine translation began in the 1950s, but it wasn’t until recent advances in artificial intelligence and computing that real-time translation became feasible. Early machine translation systems were basic, rule-based programs that translated word-for-word, often leading to awkward and inaccurate translations.
By the 1990s, statistical models improved accuracy by analyzing large datasets of translated text, but real-time translation remained a dream.
With the development of neural networks and natural language processing in the 2010s, tech giants like Google and Microsoft began creating models capable of understanding context and producing coherent translations. Today’s real-time translation devices are the result of decades of progress, combining AI with powerful processors and voice recognition to deliver high-quality translations on the spot.
Technology Behind
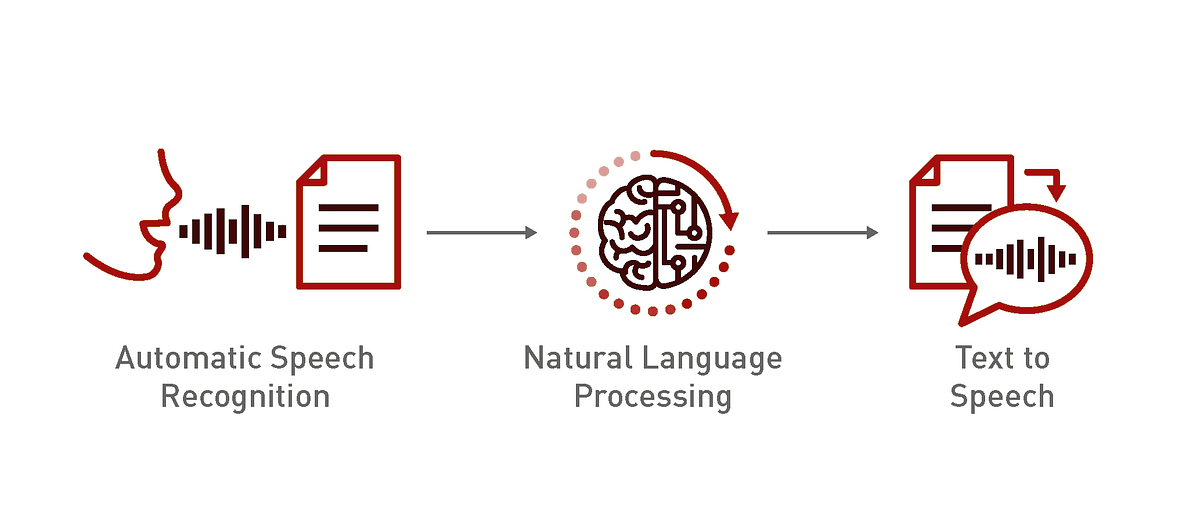
Real-time translation devices rely on AI, machine learning, and natural language processing (NLP) to translate speech or text accurately and quickly. Here’s how it works:
- Speech Recognition:
Voice translation devices use speech recognition algorithms to detect and understand spoken words. Advanced algorithms can filter out background noise and identify multiple voices, enabling accurate and smooth translations.
- Natural Language Processing:
NLP algorithms analyze and interpret the spoken language, taking into account nuances such as grammar, syntax, and context. Machine learning models use vast datasets to improve the understanding of regional dialects, idioms, and slang.
- Translation and Speech Synthesis:
The processed input is translated into the target language, and speech synthesis produces an audible output. This entire process happens within milliseconds, allowing for real-time interaction.
Some devices use cloud-based processing for fast access to extensive language databases, while others rely on on-device AI, which operates without an internet connection. This technology stack allows for translations that feel natural and conversational.
Types of
Real-Time Translation Devices & Companies
- Wearable Translators:
These include earpieces or neckbands that provide hands-free translation. Popular models, such as Google Pixel Buds and Timekettle WT2, allow users to carry on conversations without looking at a screen. Google Pixel Buds – https://support.google.com/googlepixelbuds/answer/7573100?hl=en
Google Pixel Buds – https://support.google.com/googlepixelbuds/answer/7573100?hl=en
Timekettle WT2 –https://www.timekettle.co/products/wt2-edge-online-voice-language-translator-earbuds - Handheld Translators:
Compact and easy to use, handheld devices like Pocketalk and Travis Touch translate spoken language at the press of a button. They are perfect for travelers and are capable of two-way translations in multiple languages. Travis Touch
Travis Touch - Smartphone Apps:
Apps like Google Translate and iTranslate transform smartphones into translation devices. Many apps support both text and voice translation, making them versatile tools.

- Smart Glasses:
Augmented reality (AR) smart glasses can overlay translated text on the user’s field of vision, such as on signs or documents. While still in development, devices like Vuzix AR smart glasses point to an exciting future for hands-free translations. Vuzix AR smart glasse’s new update
Vuzix AR smart glasse’s new update
Applications
Real-time translation devices have broad applications across industries:
- Travel and Tourism:
Tourists can navigate foreign countries, order food, and engage with locals confidently, enhancing their travel experience. - Business:
International businesses use these devices to facilitate multilingual meetings, enabling real-time communication between teams in different countries. - Healthcare:
Medical professionals use translation devices to communicate with patients who speak different languages, improving care and reducing misunderstandings. - Education:
Educators and students benefit from these devices by breaking down language barriers in multicultural classrooms and during exchange programs.
Benefits
The advantages of real-time translation devices are transformative:
- Enhanced Communication:
They break down language barriers, promoting mutual understanding and cultural exchange. - Improved Accessibility:
They empower individuals who don’t speak multiple languages to participate in conversations and experiences. - Global Business Enablement:
They facilitate cross-border communication, allowing companies to engage with international clients and partners without hiring interpreters. - Efficient Travel and Navigation:
Travelers can navigate foreign environments with ease, ordering food, booking services, and asking for directions without language concerns.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite significant advancements, real-time translation devices face certain limitations:
- Complexity of Language:
Dialects, idioms, and cultural references are difficult for machines to interpret accurately. Misinterpretation of these can lead to awkward or incorrect translations. - Privacy Concerns:
Cloud-based devices may store sensitive conversations, raising privacy and security issues. - Dependence on Connectivity:
Many devices require an internet connection to function optimally, which may not be available in all areas. - Battery Life:
High processing power requirements can drain device batteries quickly, especially for wearable or handheld models.
The Future
The future of real-time language translation is promising. As AI and machine learning models continue to evolve, we can expect improvements in translation accuracy, especially in capturing nuances and dialects. Wearable tech and AR are also likely to play a larger role, potentially leading to fully immersive translation experiences where language barriers feel invisible. Additionally, advancements in on-device processing could make these devices more accessible in remote areas, expanding their reach and usefulness.
Conclusion
Real-time language translation devices are reshaping how we communicate, creating new opportunities for connection in our diverse, multilingual world. From wearable earpieces to powerful smartphone apps, these devices have already made significant impacts across industries. While challenges remain, the rapid development in AI and natural language processing promises a future where language is no longer an obstacle. Real-time language translation is not just a technological marvel; it’s a bridge to a world where understanding knows no boundaries.