Beware of Money Scams: Ponzi and Pyramid Schemes Exposed
Introduction
Scammers have been deceiving people for centuries, and financial fraud has taken many forms over time. Among the most notorious scams are Ponzi and Pyramid schemes, which promise high returns but ultimately leave victims in financial ruin. With the rise of digital transactions and social media, scammers have developed even more sophisticated ways to exploit individuals. In this article, we will discuss the different types of scams, their schemes, real-life examples, and how to protect yourself from falling victim to such frauds.
Understanding Money Scams
Financial scams are fraudulent schemes designed to deceive individuals and steal their money. Scammers manipulate trust and greed to lure victims into investing in fake or unsustainable financial opportunities. The most infamous financial scams include Ponzi schemes, Pyramid schemes, and other forms of investment fraud. Understanding these scams is the first step toward protecting yourself and your finances.
-Ponzi Schemes
A Ponzi scheme is a fraudulent investment scam where returns are paid to earlier investors using funds from newer investors rather than legitimate business profits. This scam requires a constant influx of new investors to sustain payouts, making it inherently unsustainable.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ponzi-scheme_sourcefile-resized-6f8e3822259a4653b8c780eb42e67a38.jpg)
Key Characteristics:
- Promises high, guaranteed returns with little or no risk.
- Uses money from new investors to pay older investors.
- Collapses when new investors stop joining or withdrawals exceed deposits.
- No real business or profit-generating activities involved.
Example of a Ponzi Scheme:
One of the most infamous Ponzi schemes in history was run by Bernie Madoff, who scammed investors out of an estimated $65 billion. His firm promised consistent, high returns but was actually paying old investors with new investor money. When the scheme collapsed in 2008, thousands of investors lost their life savings. Another notable case involved BitConnect, a cryptocurrency scam that promised guaranteed profits through a secret trading algorithm, only to collapse when investors tried to withdraw funds en masse.
-Pyramid Schemes
A Pyramid scheme is a business model that recruits members with a promise of payments for enrolling others rather than selling legitimate products or services. Unlike Ponzi schemes, which depend on a central operator, Pyramid schemes rely on participants recruiting new members to sustain the fraud.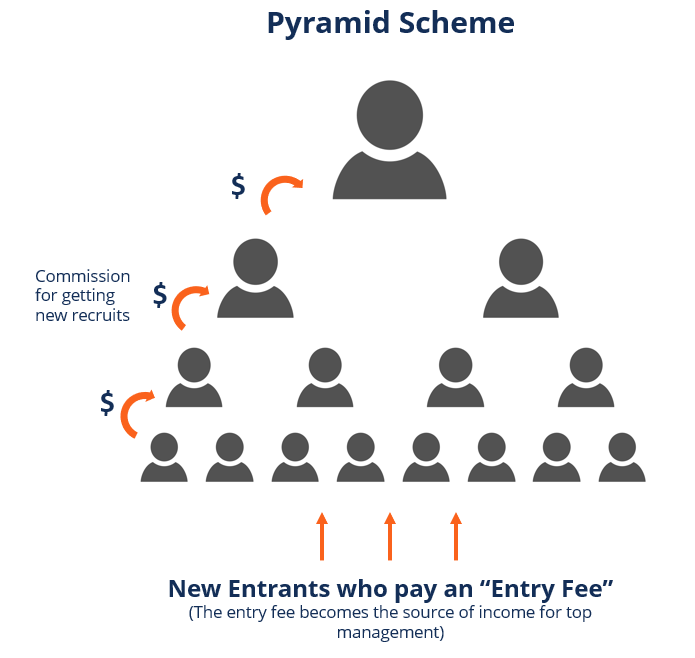
Key Characteristics:
- Requires participants to recruit others to earn money.
- Promises high returns based on recruitment rather than actual sales.
- Unsustainable, as new recruits eventually stop joining, causing the scheme to collapse.
- Often disguised as multi-level marketing (MLM) businesses.
Example of a Pyramid Scheme:
One of the most recent and widely recognized Pyramid schemes was “MMM Global”, a scam that originated in Russia and spread worldwide. It claimed to offer 30% monthly returns through a “mutual aid” system. Millions of people lost their investments when the scheme collapsed. Another example is the “WFG” (World Financial Group), which has been accused of operating as a Pyramid scheme under the guise of financial services recruitment.
Most Commonly
Used Scam Schemes
Scammers constantly evolve their tactics, but some schemes remain widely used:
1. Ponzi Schemes:
Scammers approach victims with investment opportunities promising high, consistent returns with minimal or no risk. They assure investors that the system is legal and backed by successful financial strategies. Victims are often shown fake profit reports to build trust.
- How Scammers Talk:
“This investment has been providing 20% returns every month for years. It’s completely safe, and you can withdraw anytime. Trust me, this is how the wealthy grow their money!” - Real Example:
Bernie Madoff’s Ponzi scheme, which lasted for decades before collapsing, ruining thousands of investors.
2. Pyramid Schemes:
Recruiters present opportunities that sound like legitimate business ventures, convincing people to bring in new members in exchange for commissions. They claim that the more people you recruit, the more money you earn.
- How Scammers Talk:
“This is not a pyramid scheme; it’s a once-in-a-lifetime business opportunity! You just need to invite a few friends, and you’ll be earning passive income in no time.” - Real Example:
The “MMM Global” scam tricked millions worldwide into investing in a fake mutual aid system before collapsing.
3. Get-Rich-Quick Scams:
These scams promise instant wealth with minimal effort, such as flipping small investments into massive returns overnight.
- How Scammers Talk:
“Double your money in just 24 hours! All you have to do is send $500, and I’ll turn it into $5000 instantly.“ - Real Example:
Many Instagram and WhatsApp-based fraudsters use this trick to lure victims into depositing money into fraudulent accounts.
4. Forex and Crypto Scams
Scammers claim to be expert traders offering secret trading strategies that guarantee high profits. They often use fake testimonials and manipulated profit charts.
- How Scammers Talk:
“Join my VIP crypto trading group, and I will show you how to earn $10,000 every week. Just invest $200 to get started!” - Real Example:
Fake crypto investment websites that promise high returns but disappear after collecting large sums from investors.
5. Fake Job Offers
Fraudsters advertise high-paying jobs but ask for upfront fees for training materials, background checks, or work permits.
- How Scammers Talk:
“Congratulations! You’ve been selected for a high-paying online job. Just pay a small $50 processing fee to get started.” - Real Example:
Many fake remote job postings on social media that ask for upfront payments from job seekers.
6. Lottery and Prize Scams
Victims receive fake notifications claiming they have won a lottery or prize but need to pay taxes or processing fees to claim it.
- How Scammers Talk:
“You’ve won $1,000,000! Just send us a small $100 fee to cover processing charges, and we’ll transfer the money to your account.” - Real Example:
Many scammers impersonate well-known companies like Facebook or Google to trick people into sending money for fake prizes.
7. Online Romance Scams
Scammers create fake online identities and build emotional relationships with victims, eventually asking for money for emergencies.
- How Scammers Talk:
“I love you, but I’m stuck in a financial crisis. I need $2000 to come visit you; can you help me?” - Real Example:
Many fraudsters use dating apps or social media to exploit lonely individuals.
8. Charity Scams
Fake charities trick people into donating money by using emotional stories and fake images.
- How Scammers Talk:
“Children are starving in this country; we need your urgent donation. Every dollar helps!” - Real Example:
Scammers set up fake GoFundMe or crowdfunding pages to steal money from generous donors.
9. Tech Support Scams
Victims receive fake warnings that their computers are infected, and they must pay for unnecessary or fake repairs.
- How Scammers Talk:
“Your computer has a serious virus! Call our tech support team immediately and pay $299 for removal.” - Real Example:
Scammers pose as Microsoft or Apple support and convince people to install malware on their devices.
10. Social Media and Influencer Scams
Fraudulent giveaways, fake endorsements, and impersonation of celebrities trick users into sharing personal data or making payments.
- How Scammers Talk:
“Win a free iPhone! Just send a $50 processing fee to claim your prize.” - Real Example:
Fake social media pages pretending to be influencers and celebrities, luring followers into fake giveaways.
How to Protect Yourself from Scams
Scammers use manipulation and psychological tricks to lure victims. Here’s how you can protect yourself:
- Be skeptical of unrealistic promises –
If an investment sounds too good to be true, it probably is. - Verify legitimacy –
Check company registrations, licenses, and customer reviews before investing. - Avoid pressure tactics –
Scammers often create urgency to force quick decisions. - Do independent research –
Don’t rely solely on what promoters tell you. - Check for transparency –
Legitimate businesses disclose how they generate revenue. - Report suspicious activities –
If you suspect a scam, report it to authorities. - Use secure payment methods –
Avoid sending money via untraceable methods like gift cards or cryptocurrency. - Stay informed –
Keep up to date with common scams and fraud tactics to avoid becoming a victim.
Conclusion
By recognizing red flags and staying informed, you can protect yourself and others from scams. Always question too-good-to-be-true offers and report suspicious activities to prevent further fraud.
Remember: If something sounds too good to be true, it probably is!
(Click notification ![]() for more updates)
for more updates)
Artical was written by V.Harishram
''Stay true, bring facts to you''

