Artificial Intelligence (AI) has moved from science fiction into real-world applications, dramatically changing industries, enhancing human capabilities, and shaping the future. From chatbots and recommendation algorithms to autonomous vehicles and predictive analytics, AI is a pervasive force driving technological innovation. But what exactly is AI, and how did we get here? This article will explore AI’s evolution, its different types, the companies leading the charge, and the technology’s current and future impact.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to mimic cognitive functions such as learning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. At its core, AI is about creating machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing speech, interpreting images, or playing games. AI operates through algorithms, data processing, and models that enable machines to improve their performance over time.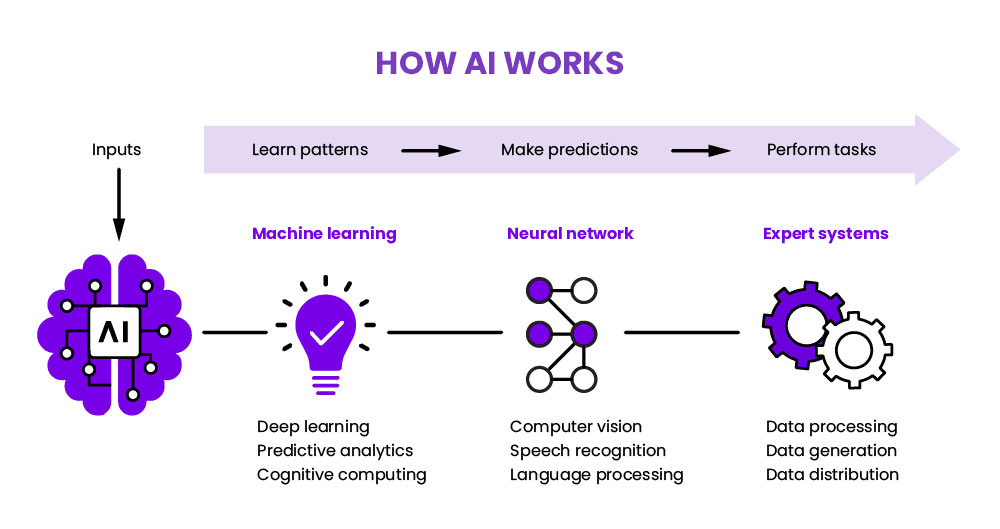
The History of AI
The concept of artificial intelligence has been around for centuries, but its modern history began in the mid-20th century. Here’s a brief overview:
- 1950s-1960s:
British mathematician Alan Turing laid the groundwork for AI with his paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” in 1950, where he proposed the Turing Test to determine a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior. Early AI research focused on symbolic logic, reasoning, and simple problem-solving programs. - 1970s-1980s:
Expert systems, which were designed to simulate the decision-making ability of human experts, emerged during this period. However, limitations in computing power and knowledge representation led to what is often referred to as the “AI Winter“—a period where interest and investment in AI research waned. - 1990s-2000s:
The development of machine learning, combined with greater computational power, brought AI back to prominence. IBM’s Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997, marking a significant milestone. - 2010s-Present:
The rise of big data, cloud computing, and breakthroughs in deep learning have propelled AI into the mainstream. AI technologies now power applications in healthcare, finance, automotive, and more, driven by companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon.
Types of AI:
ANI, AGI, ASI, and Beyond
AI can be classified into three main categories based on its scope and capabilities:
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI):
Also known as “Weak AI,” ANI is designed to perform specific tasks. Examples include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, recommendation algorithms on Netflix, and spam filters in email systems. ANI systems cannot perform beyond their predefined tasks and have no general understanding of the world.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI):
AGI, or “Strong AI,” refers to machines that possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply intelligence across a wide range of tasks, similar to a human being. AGI remains theoretical at this point, as no system currently exists with the broad cognitive capabilities of humans.
- Artificial Superintelligence (ASI):
ASI is a hypothetical level of AI that surpasses human intelligence in all respects. It could potentially perform any intellectual task better than a human, from scientific reasoning to emotional intelligence. While ASI is still speculative, its potential raises significant ethical and safety concerns about the future of AI.
AI Companies Leading the Way
Several companies are at the forefront of AI development, pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve:
- Google DeepMind:
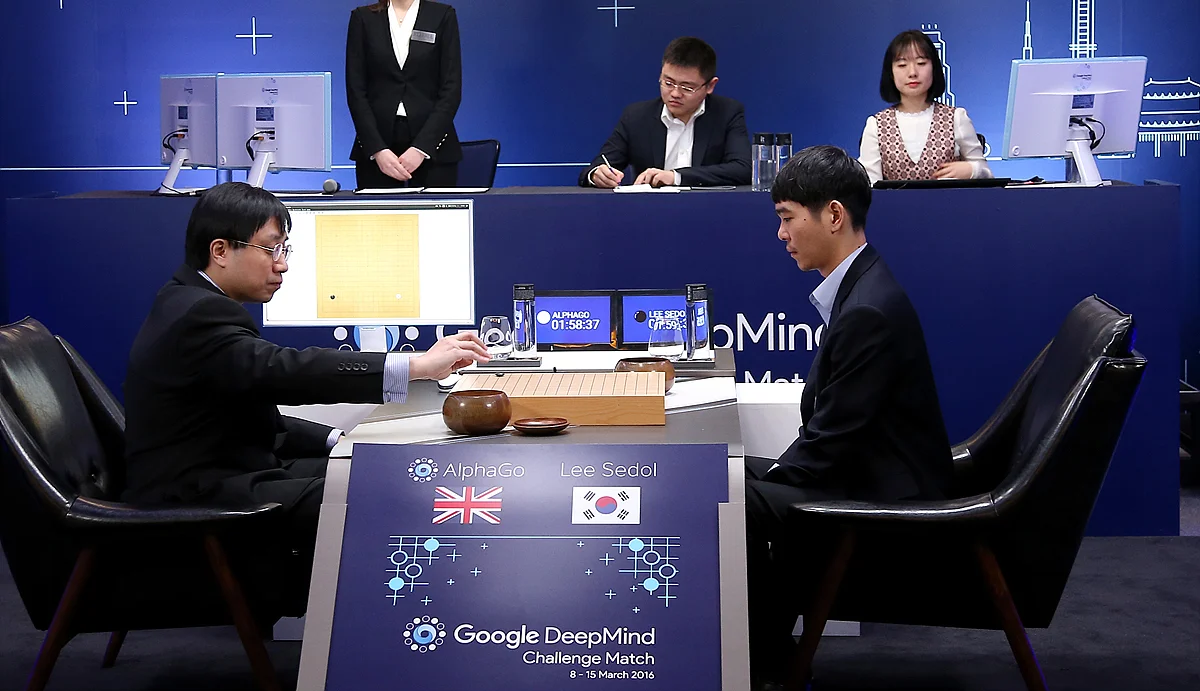
Known for its groundbreaking work in reinforcement learning and neural networks, DeepMind gained fame when its AI, AlphaGo, defeated the world champion in the game of Go. The company continues to lead in AI research with a focus on complex problem-solving. - OpenAI:
OpenAI is a key player in the AI space, known for its advanced natural language processing models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer). These models are behind the powerful text generation and conversational capabilities seen in applications like ChatGPT.
- IBM Watson:
IBM’s AI platform, Watson, is widely used in industries like healthcare, finance, and legal services for its ability to process vast amounts of data and deliver insights.
- Microsoft:
Through its Azure AI platform and investment in AI research, Microsoft is pioneering in areas like natural language processing, vision, and decision-making systems.
- NVIDIA:
While primarily a hardware company, NVIDIA’s GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are integral to AI research, particularly in deep learning and AI-driven simulations.
Trending AI Technologies
Several AI technologies are gaining traction and driving innovation across industries:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP enables machines to understand and generate human language. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and advanced language models like GPT-4 use NLP to deliver seamless conversational experiences.
- Computer Vision:
This technology allows machines to interpret and understand the visual world. From facial recognition to autonomous driving, computer vision applications are vast and growing. - Deep Learning:
Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, involves neural networks with many layers that can model complex patterns in data. This technology has enabled major breakthroughs in image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems. - Reinforcement Learning:
Reinforcement learning involves AI agents learning to make decisions by interacting with their environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. It has applications in robotics, gaming, and automation.
AI Usage Across Industries
AI is now being used across multiple sectors, improving efficiency, decision-making, and customer experiences:
- Healthcare: AI systems assist in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images, and even predicting patient outcomes. AI is also accelerating drug discovery by identifying promising compounds more quickly.
- Finance:
AI is used for fraud detection, risk management, algorithmic trading, and customer service chatbots. It can analyze large datasets to detect patterns that humans might miss. - Retail:
AI-driven recommendation systems personalize the shopping experience for customers, while AI algorithms optimize inventory management and demand forecasting. - Transportation:
Autonomous vehicles rely on AI to interpret sensor data, make driving decisions, and improve safety. AI also powers traffic management systems and predictive maintenance in the transportation industry. - Manufacturing:
AI is streamlining production processes, improving quality control, and reducing downtime through predictive maintenance in manufacturing environments.
Benefits of AI
- Automation of Routine Tasks:
AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative activities. - Improved Decision-Making:
AI systems can analyze large volumes of data, uncovering insights and patterns that humans may not easily detect. - Increased Efficiency:
AI-powered automation can reduce operational costs and enhance productivity, particularly in industries like manufacturing and logistics. - Enhanced Personalization:
AI-driven recommendations and personalized services improve customer experiences in retail, entertainment, and healthcare.
Disadvantages of AI
- Job Displacement:
As AI automates tasks traditionally done by humans, certain jobs are at risk of being replaced, leading to concerns about unemployment and inequality. - Bias and Fairness:
AI systems can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to unfair outcomes, especially in areas like hiring, criminal justice, and lending. - Privacy Concerns:
AI systems often rely on large amounts of personal data, raising concerns about data privacy and security. - Ethical Dilemmas:
As AI becomes more powerful, ethical questions arise about its impact on decision-making, autonomy, and the potential for misuse in surveillance or warfare.
The Future of AI
The future of AI holds both promise and challenges. Advances in areas like quantum computing and neuromorphic engineering may unlock new capabilities, while ongoing research in AI ethics will shape how we integrate these systems into society. AI will likely continue transforming industries, solving complex global problems, and enabling new possibilities for human-machine collaboration.ch

However, as AI progresses toward AGI or even ASI, careful consideration of the ethical and societal impacts is crucial. Ensuring that AI technologies are developed responsibly, transparently, and inclusively will be key to maximizing their benefits while minimizing risks.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence has evolved from a futuristic concept into a practical, everyday tool that is reshaping industries and society. While the benefits of AI are clear—from automating routine tasks to driving innovation—the challenges it presents, including job displacement and ethical concerns, must be addressed. As AI continues to evolve, it will likely play an even more central role in our lives, bringing both opportunities and responsibilities for developers, businesses, and policymakers. The key to AI’s future lies not just in technological advancement but in thoughtful governance and ethical use.