As we seek sustainable solutions to meet the growing energy demands of the modern world, space-based solar power (SBSP) has emerged as an innovative approach. By collecting solar energy from space and transmitting it to Earth, SBSP could potentially offer an unlimited supply of clean energy, unaffected by terrestrial constraints. Although still in developmental stages, SBSP is a promising prospect with significant implications for the future of energy.
What is Space-Based Solar Power?
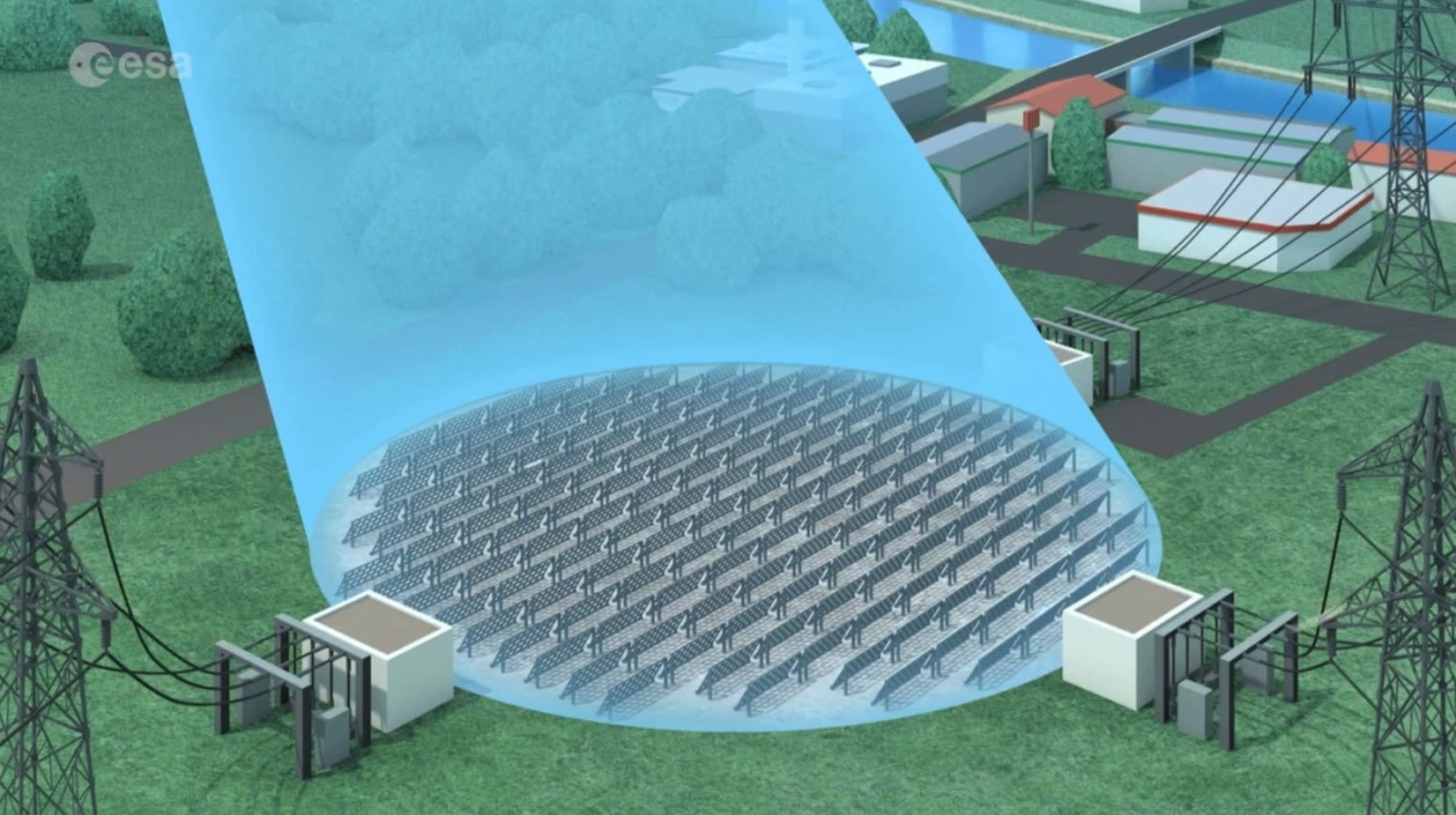
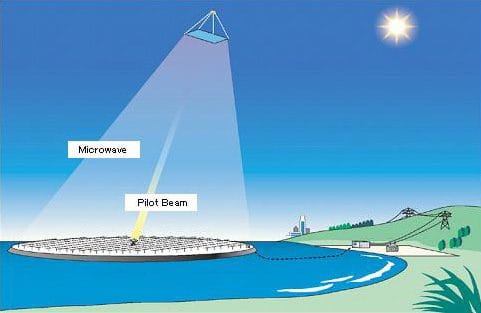
Space-Based Solar Power is a method of collecting solar energy directly from space and delivering it to Earth. Unlike traditional solar power, which relies on ground-based solar panels exposed to sunlight only during the day, SBSP uses solar collectors placed on satellites in orbit. These orbiting solar farms capture sunlight 24/7, converting it into microwave or laser energy. The energy is then transmitted wirelessly to ground-based receiving stations, known as rectennas, where it is converted back into electricity and fed into the power grid.
Technology Behind SBSP
SBSP technology encompasses three main components:
- Solar Energy Collection:
Solar panels are mounted on satellites in geostationary orbit, approximately 36,000 kilometers above the Earth. In this orbit, satellites remain stationary relative to a specific location on the Earth’s surface, allowing for continuous solar energy collection.
- Energy Conversion and Transmission:
The solar energy captured by these satellites is converted into microwave or laser beams, chosen for their efficiency in transferring energy over long distances. Microwaves are particularly suitable because they can penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere without interference, minimizing energy loss.
- Energy Reception on Earth:
The microwaves or laser beams are directed toward large ground-based rectennas, where the energy is converted back into electricity. This electricity is then integrated into the existing power grid for distribution and use.
Current Use of
Space-Based Solar Power
While SBSP has not yet been fully implemented on a large scale, several countries and agencies are actively exploring its potential:
- Japan:
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) has been working on SBSP projects for years and has successfully demonstrated wireless power transmission over short distances. JAXA’s long-term vision includes a fully operational SBSP system that could be deployed by the mid-2030s. https://www.kenkai.jaxa.jp/eng/research/ssps/ssps-ssps.html
https://www.kenkai.jaxa.jp/eng/research/ssps/ssps-ssps.html - China:
China has announced ambitious plans to launch a prototype SBSP system in the 2020s and aims for a fully operational power station in space by 2050. The Chinese government views SBSP as a strategic technology that could support the country’s growing energy demands.
- United States:
NASA has conducted multiple feasibility studies on SBSP, and several private companies are working on similar technology. Some companies are focused on developing small-scale SBSP systems to power remote or off-grid locations, providing a preview of SBSP’s future applications.
Advantages of
Space-Based Solar Power
- Continuous Energy Supply:
By collecting solar energy in space, SBSP systems are not limited byweather or the day-night cycle, allowing for an uninterrupted energy supply. - High Efficiency and Energy Density:
Satellites in space receive more sunlight than ground-based solar panels, as they avoidatmospheric and seasonal variations. This increased solar exposure allows SBSP systems to generate more energy with fewer solar panels. - Reduced Land Use:
Space-based energy collection reduces the need forlarge land-based solar farms,freeing up valuable land resources and minimizing environmental impact. - Energy Access for Remote Areas:
SBSP has the potential to provide energy to regions without developedpower infrastructure, offering a reliable source of electricity for remote or underserved communities.
Challenges Facing
Space-Based Solar Power
While SBSP holds significant promise, there are notable challenges that must be addressed before it can become a mainstream energy source:
- High Initial Costs:
Building and launching satellites with solar panels into space is costly, especially with current rocket technology. The cost of developing large-scale SBSP infrastructure could be a barrier to widespread adoption. - Wireless Energy Transmission:
Transmitting energy wirelessly from space to Earth is technically challenging, particularly over long distances. Although microwave transmission is efficient, ensuring precise targeting and safe transmission requires further research and development. - Public and Environmental Safety Concerns:
High-power microwave transmission raises questions about potential effects on human health, wildlife, and the environment. These concerns will need to be carefully addressed to ensure the safety of SBSP technology. - International Regulation and Collaboration:
As a global technology, SBSP would likely involve collaboration between multiple countries. Establishing clear regulations, including frequency allocation and orbital slots, will be essential to prevent conflicts and ensure equitable access.
Future Prospects of
Space-Based Solar Power
The future of SBSP appears bright, with growing interest and investment from governments and private entities alike. Technological advances in reusable rockets, wireless energy transmission, and satellite design are paving the way for SBSP to become a feasible energy solution within the next few decades.
Experts predict that SBSP could initially serve specific, high-cost areas like military bases or remote locations. Eventually, as technology matures and costs decrease, SBSP could become an integral part of the global energy landscape, supplying power to entire cities and even countries.
If successful, SBSP could be used to power data centers, urban transportation networks, and industrial complexes, among other applications. With its ability to deliver uninterrupted, high-density energy, SBSP has the potential to transform the energy sector and significantly reduce global reliance on fossil fuels.
Conclusion
Space-Based Solar Power represents a bold and innovative vision for the future of energy. By capturing solar energy in space and transmitting it wirelessly to Earth, SBSP offers a renewable energy source that could power the world around the clock. While there are challenges to overcome—including high costs, technical hurdles, and regulatory considerations—the benefits of SBSP are undeniable. As countries and companies invest in research and development, SBSP may one day become a cornerstone of sustainable energy.
With its potential to provide abundant, clean, and accessible energy, SBSP stands poised to play a pivotal role in the fight against climate change and energy poverty. If fully realized, it could propel humanity into an era of unprecedented energy independence, offering a sustainable solution for a brighter, greener future 🙂